Remote Sensing to Answer Tomorrow’s World Peace Today
NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites; twin satellites were launched in March 2002 are making detailed measurements of Earth’s gravity field which will lead to discoveries about gravity and Earth’s natural systems. These discoveries could have far-reaching benefits to society and the world’s population.
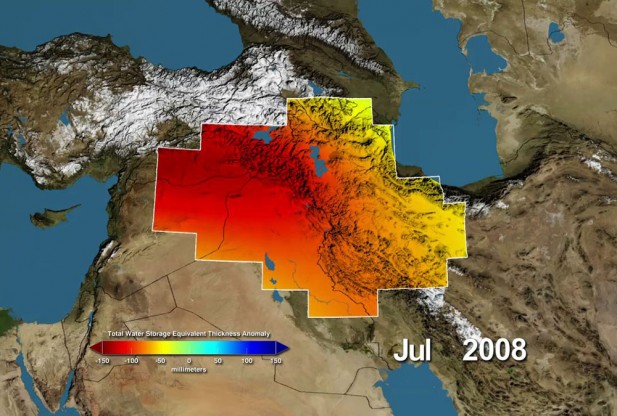
Previously scientists have presented the fresh water risk in India. They have attributed the India’s water storage loss as the fastest rate of groundwater storage loss. Recently, another study using data from a pair of gravity-measuring (GRACE) satellites, finds that a large part of the arid Middle East region has lost the fresh water reserves rapidly during the past decade. The researchers have used GRACE satellite images for the period (2003-2009) and successfully identified the water loss in the parts of Turkey, Syria, Iraq and Iran along the Tigris and Euphrates river basin. They have found this region was losing around 117 million acre feet of fresh water, which is about the equivalent to the Dead Sea. ops! Quite an alarm.

Variations in total water storage from normal, in millimeters, in the Tigris and Euphrates river basins, as measured by NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites, from January 2003 through December 2009. Reds represent drier conditions, while blues represent wetter conditions. The majority of the water lost was due to reductions in groundwater caused by human activities. By periodically measuring gravity regionally, GRACE tells scientists how much water storage changes over time. Image Credit: NASA / UC Irvine / NCAR
Some researchers have attributed the causes of the rapid decline of water reserves are pumping of groundwater from underground reservoirs and drought. If i want to put a little technical detail how this system works, we can explain like; drought controls the ground water recharge and ground water storage controls the earth’s gravity field and monitoring the earth’s gravity field we can estimate the change in ground water reserve.
Now, what about the water storage trends of the whole world? I’m truly excited to know about that. Because some conflict researchers are assuming that the next world war will be over the access to the fresh water, which can be found in several Environmental security literature. If it’s true, this kind of critical piece of information on fresh water can secure tomorrow’s world peace. Whenever we talk about fresh water resource the climate change hops in. Global warming is not only warming us up its also snatching out water resource and causing droughts. What’s the scenario then? Though fragile but a clear understanding is countries in lower latitude (i.e., Sub-Saharan Africa) are suffering from global warming and the face is drought It would be interesting to assess the ground water loss from both of the cause windows (pumping water and drought) separately.Until now, GRACE really is the only way we can estimate groundwater storage changes from space. GRACE images and Uppsala Conflict Data Program’s Georeferenced Event Dataset are the way out to conduct such research. Now, we all know issues and methods; lets save the world.
source: http://www.nasa.gov/grace